Publication on MDPI Sensors
Vision-Based Hybrid Controller to Release a 4-DOF Parallel Robot from a Type II Singularity
During my Internship in ai2.upv I contributed to a research paper that was also part of my Master's Thesis. The paper was published in MDPI Sensors and it is available here. I contributed by implementing the proposed novel controller, which also makes use of control architecture that I implemented in ROS2 with C++ (mostly) and Python.
This paper introduces a novel hybrid controller for a 4-DOF parallel robot that is able to detect when the robot is in a type II singular position and brings the robot back to a safe configuration. This is very important in the context of rehabilitation robots, since there is the possibility of losing control of the robot and making the robot not safe enough for a patient. Solving this type of issues would make a parallel robot more suitable for rehabilitation purposes because they have the advantages of
having a high accuracy as well as a better dynamic performance than serial robots.
This particular controller uses a external sensor to track the position and orientation of the platform. The external sensor used was the motion capture system Optitrack. So I implemented first a driver to be able to read the data coming from Optitrack and be able to feed the controller with the cartesian pose of the platform. The arrangement of the cameras in the laboratory can be seen in the following image:
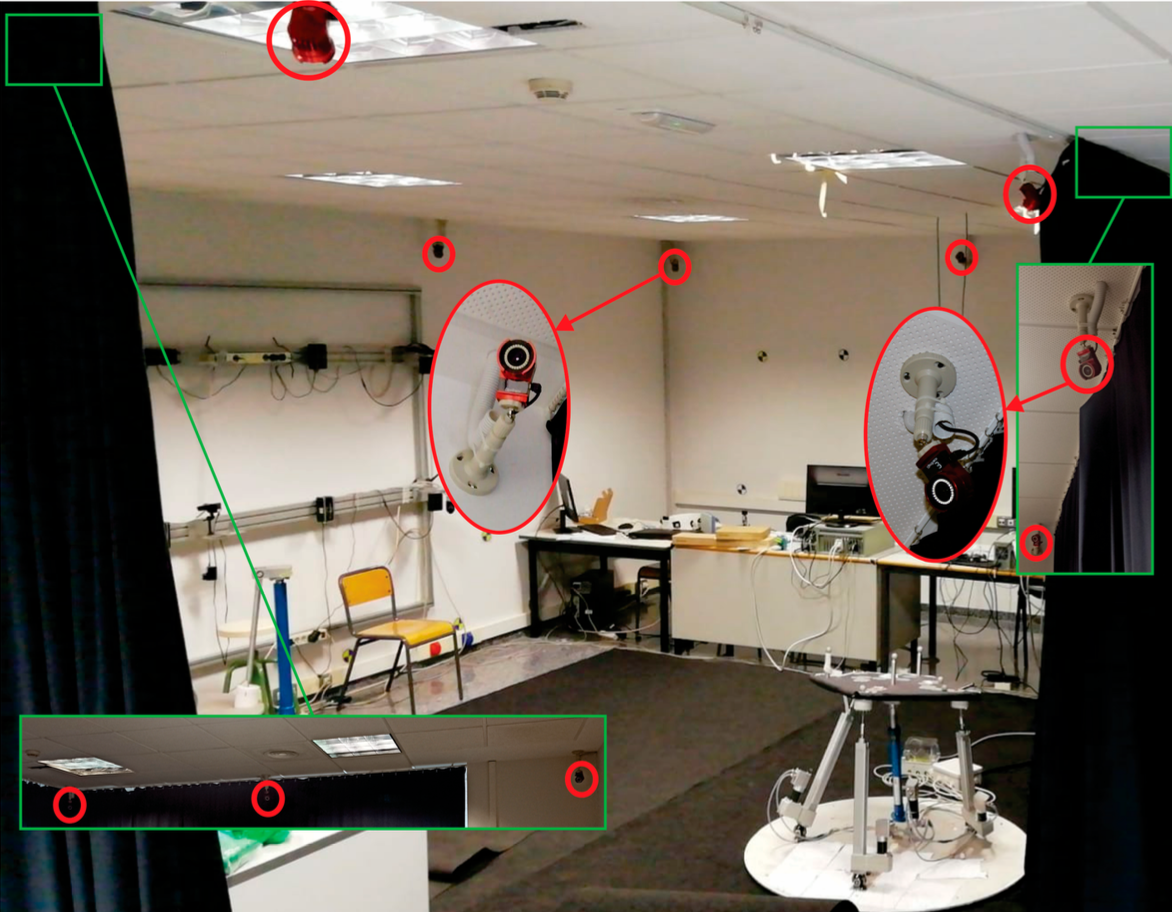

There is this need of having an external sensor because computing Forward Kinematics based on the joint sensors is not possible in a singular position because computing the Jacobian matrix would have numerical innestabilities. As a reminder, Forward Kinematics is the difficult problem in parallel robots (opposite to serial where the difficult one is Inverse Kinematics) and we need a Numerical algorithm that makes use of the Jacobian matrix. After this, the Type II Singularity Control Module was able to work on top of the position controller to detect first if the robot was in a Type II Singular position and release the robot from this configuration. The control scheme can be visualized in the following diagram:
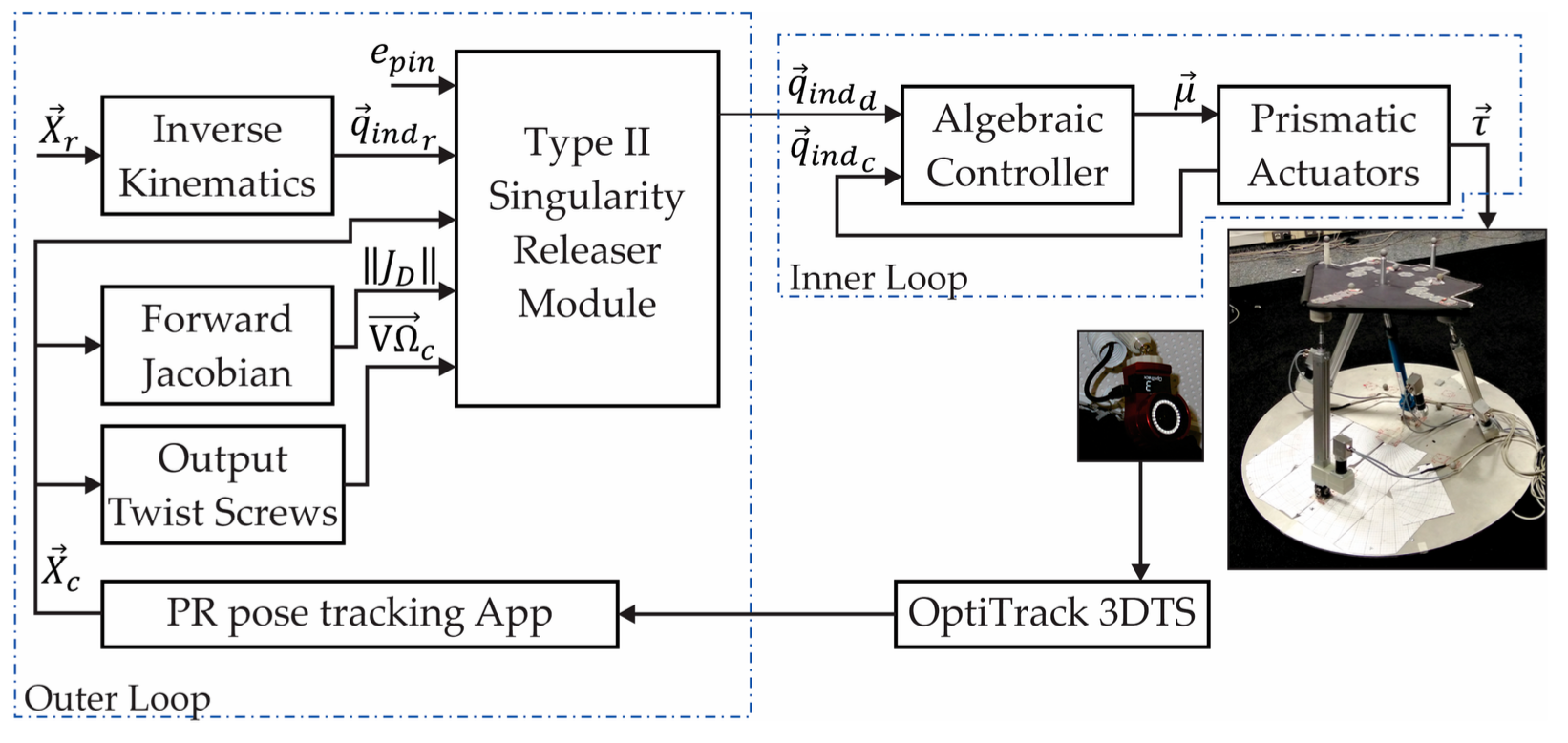
Finally, a demonstration of the controller working on the real robot can be seen in this video:
Reference:
Vision-Based Hybrid Controller to Release a 4-DOF Parallel Robot from a Type II Singularity
- José L. Pulloquinga
- Rafael J. Escarabajal
- Jesús Ferrándiz
- Marina Vallés
- Vicente Mata
- Mónica Urizar